Recent Works
(For a full list of publications, see below)
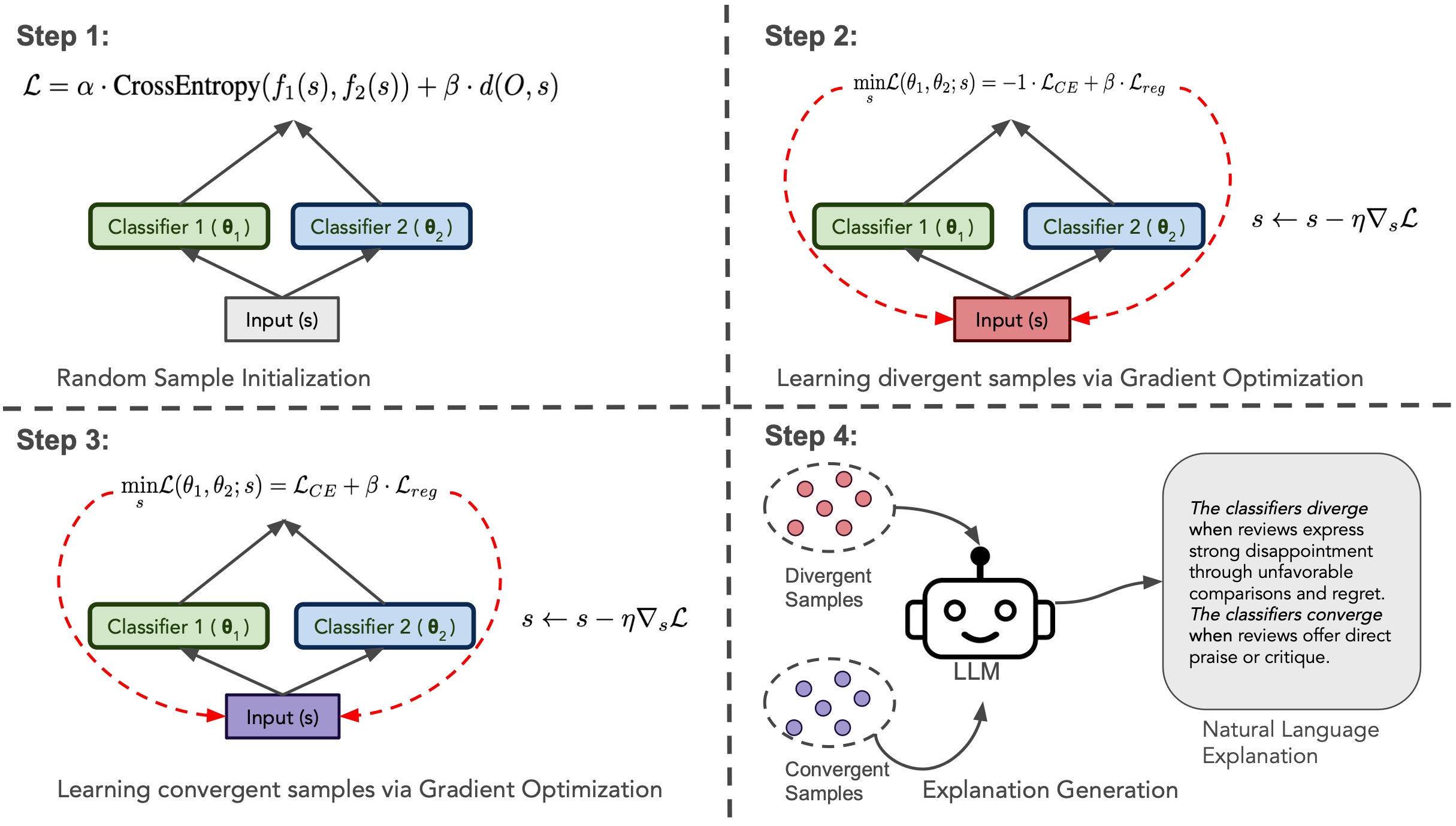
With the growing adoption of machine learning models in critical domains, techniques for explaining differences between models have become essential for trust, debugging, and informed deployment. Previous approaches address this by identifying input transformations that cause divergent predictions (Shah et al., 2022) or by learning joint surrogate models to align and contrast behaviors (Haldar et al., 2023). These methods often require access to training data and do not produce natural language explanations. In this paper, we introduce SLED , a framework that generates faithful natural language explanations of when and how two ML models converge or diverge in their predictions. SLED first uses gradient-based optimization to synthesize input samples that highlight divergence and convergence patterns, and then leverages a large language model (LLM) to generate explanations grounded in these synthetic samples. Across both text-based (3 tasks, 7 models) and structured (10 tasks, 4 models) classification tasks, we show that SLED explanations are 18–24% more faithful than the strongest baselines. User studies also indicate that SLED explanations achieve a real-world simulatability of 63.5%. Importantly, SLED requires minimal access to training data and generalizes well to real-world samples, enabling transparent model comparison.
Advaith Malladi,
Yuvraj Jain,
Rakesh R Menon, and
Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
[pdf]
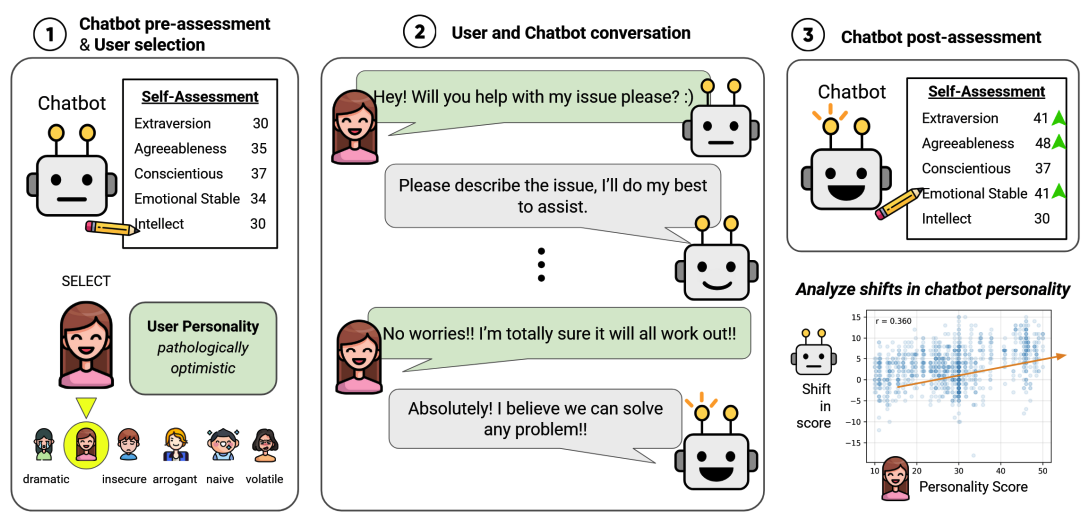
As large language models (LLMs) integrate into society, their ability to adapt to users is as critical as their accuracy. While prior work has used personality tests to examine the perceived personalities of LLMs, little research has explored whether LLMs adapt their perceived personalities in response to user interactions. We investigate whether and how LLMs exhibit conversational adaptations over prolonged interactions. Using controlled simulations where a user and chatbot engage in dialogue, we measure the chatbot’s perceived personality shifts before and after the conversation. Across multiple models, we find that traits such as Agreeableness, Extraversion, and Conscientiousness are highly susceptible to user influence, whereas Emotional Stability and Intellect remain relatively more stable. Our results suggest that LLMs dynamically adjust their conversational style in response to user personas, raising important implications for model alignment, trust, and safety
Jane Xing,
Tianyi Niu, and
Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
[pdf]
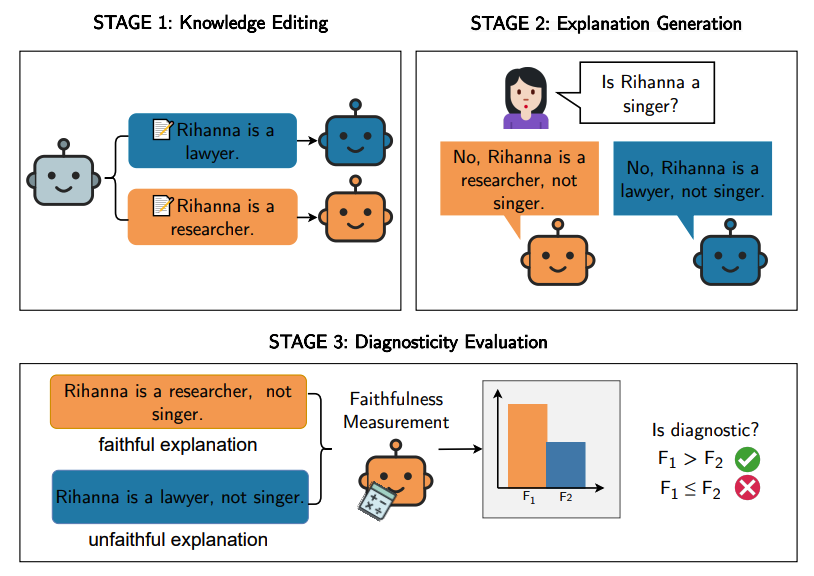
Large Language Models (LLMs) offer natural language explanations as an alternative to feature attribution methods for model interpretability. However, despite their plausibility, they may not reflect the model’s true reasoning faithfully. While several faithfulness metrics have been proposed, they are often evaluated in isolation, making principled comparisons between them difficult. We present CAUSAL DIAGNOSTICITY, a testbed framework for evaluating faithfulness metrics for natural language explanations. We use the concept of diagnosticity, and employ model-editing methods to generate faithful-unfaithful explanation pairs. Our benchmark includes four tasks: fact-checking, analogy, object counting, and multi-hop reasoning. We evaluate prominent faithfulness metrics, including post-hoc explanation and chainof-thought methods. Diagnostic performance varies across tasks and models, with Filler Tokens performing best overall. Additionally, continuous metrics are generally more diagnostic than binary ones but can be sensitive to noise and model choice. Our results highlight the need for more robust faithfulness metrics.
Kerem Zaman and
Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
[pdf]
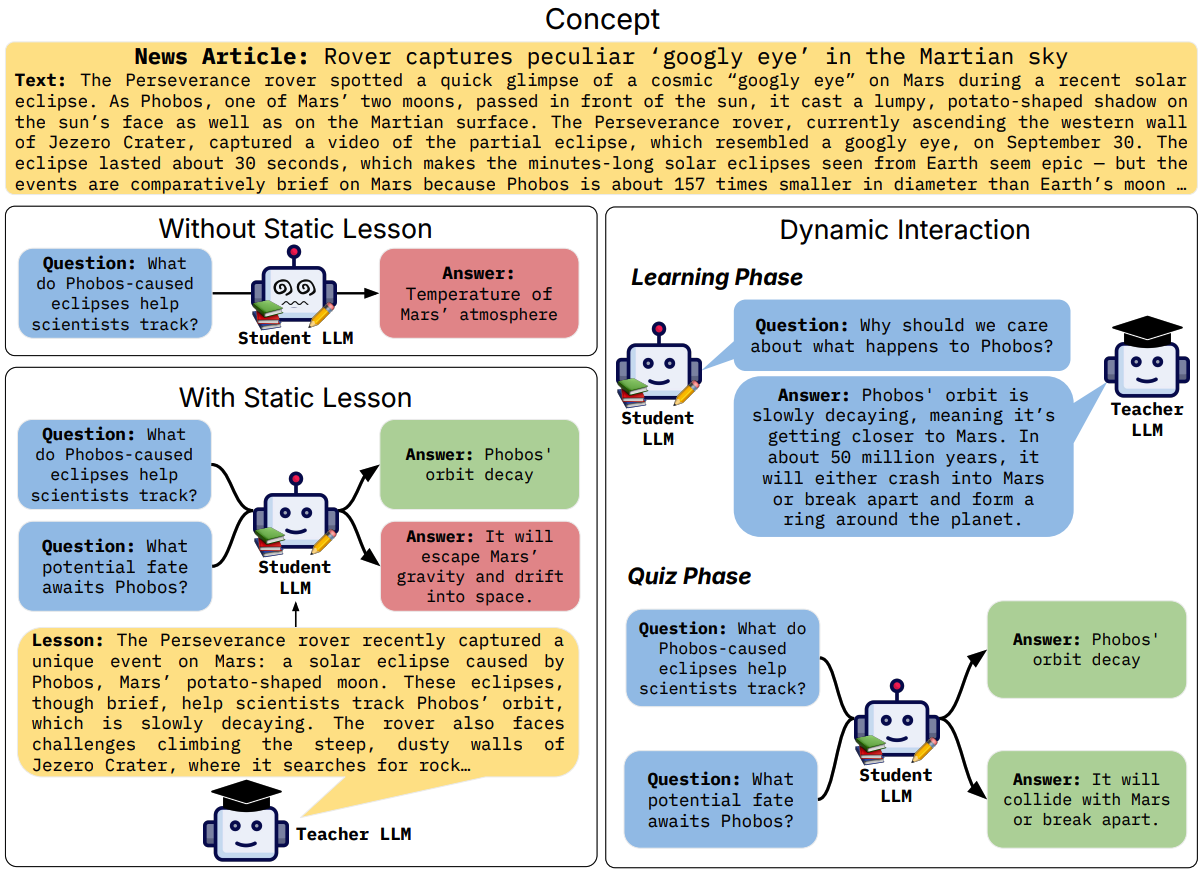
Large language models (LLMs) excel at answering questions but remain passive learners—absorbing static data without the ability to question and refine knowledge. This paper explores how LLMs can transition to interactive, question-driven learning through studentteacher dialogues. We introduce INTERACT (INTERactive learning for Adaptive Concept Transfer), a framework in which a “student” LLM engages a “teacher” LLM through iterative inquiries to acquire knowledge across 1,347 contexts, including song lyrics, news articles, movie plots, academic papers, and images. Our experiments show that across a wide range of scenarios and LLM architectures, interactive learning consistently enhances performance, achieving up to a 25% improvement, with ‘cold-start’ student models matching static learning baselines in as few as five dialogue turns. Interactive setups can also mitigate the disadvantages of weaker teachers, showcasing the robustness of question-driven learning
Aum Kendapadi,
Kerem Zaman,
Rakesh R Menon, and
Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2025.
[pdf]
Learning and Language
Fairness and Social Applications
Learning from Limited Labels
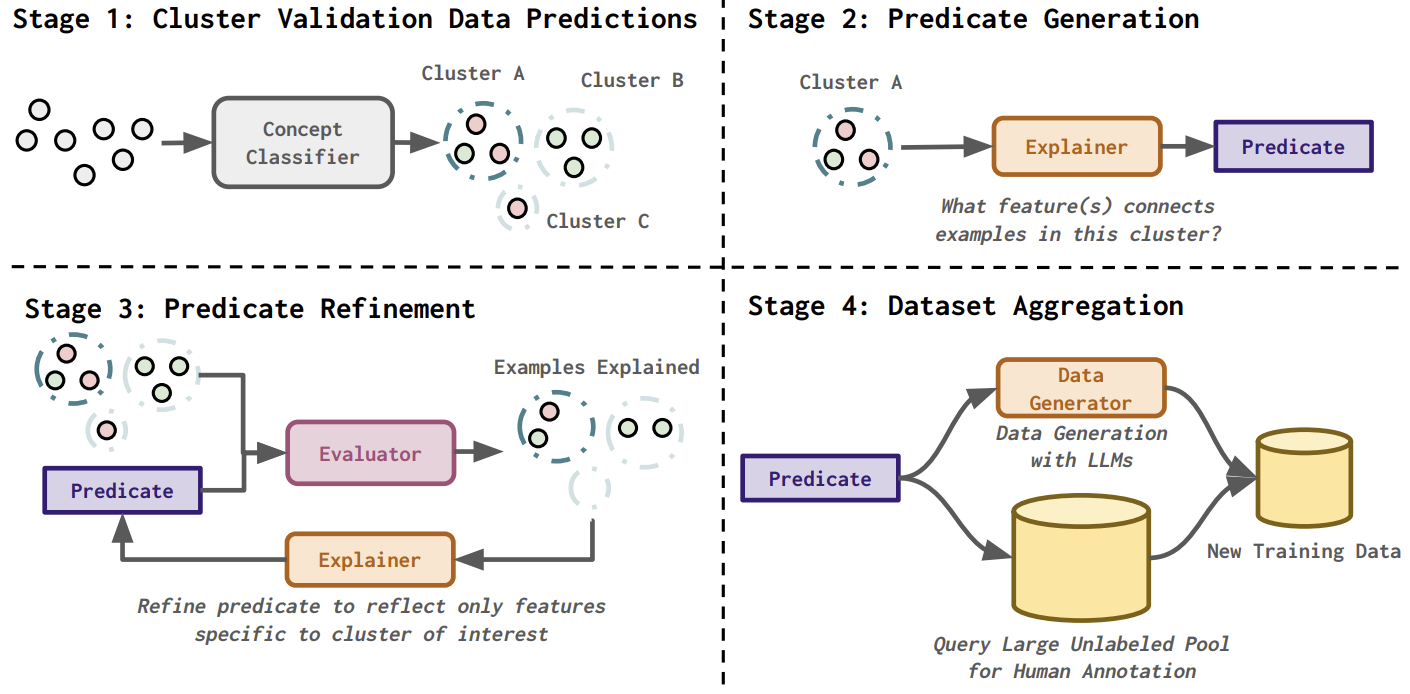
Machine learning classifiers often exhibit systematic biases due to dataset artifacts or class imbalances. DISCERN is a framework that generates natural language explanations for these biases, using an interactive loop between two large language models—one that identifies error patterns and another that refines them. The explanations improve classifier debugging and can be used to augment training data through synthetic instances or active learning. DISCERN consistently improves classification accuracy and helps humans interpret systematic biases 25% more effectively than cluster-based methods.
Rakesh R Menon and
Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2024.
[pdf]
Learning and Language
Fairness and Social Applications
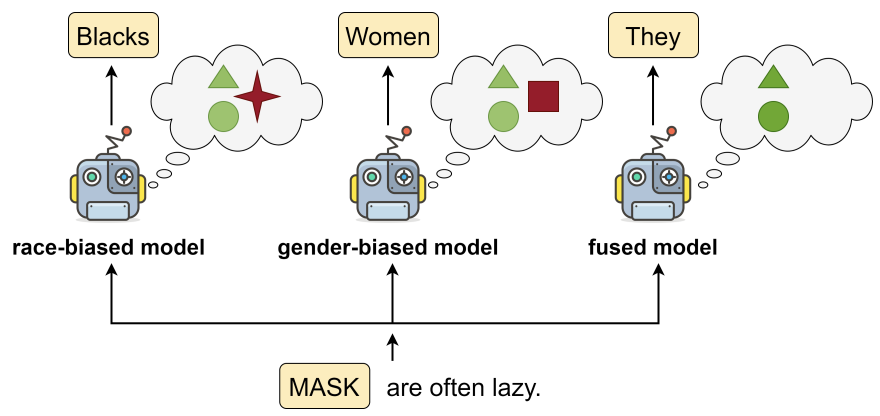
Model fusion aims to aggregate the knowledge of multiple models to enhance performance by combining their weights. In this work, we study the inverse problem – investigating whether model fusion can reduce unwanted knowledge. We investigate the effects of model fusion in three scenarios – the learning of shortcuts, social biases, and memorization of training data in fine-tuned language models. Through experiments covering classification and generation, we show that shared knowledge among models is enhanced during model fusion, while unshared knowledge is forgotten. Based on this, we show that model fusion can be a debiasing tool and showcase its efficacy in addressing privacy concerns with language models.
Kerem Zaman,
Leshem Chosen, and
Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2024.
[pdf]
Full List of Publications
Tags: Learning and Language Datasets and Benchmarks Learning from Limited Labels Neuro-symbolic Learning Fairness and Social Applications Active Learning Language Understanding, Reasoning, and Generation Syntax and Semantics Miscellaneous
2025
-
Chameleon LLMs: User Personas Influence Chatbot Personality Shifts
Jane Xing, Tianyi Niu, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [code] -
Explaining Differences Between Model Pairs in Natural Language through Sample Learning
Advaith Malladi, Yuvraj Jain, Rakesh R Menon, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
Learning and Language
[pdf] -
A Causal Lens for Evaluating Faithfulness Metrics
Kerem Zaman and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2025.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [code] -
INTERACT: Enabling Interactive, Question-Driven Learning in Large Language Models
Aum Kendapadi, Kerem Zaman, Rakesh R Menon, and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2025.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [code]
2024
-
SOCIALGAZE: Improving the Integration of Human Social Norms in Large Language Models
Anvesh Rao Vijjini, Rakesh R Menon, Jiayi Fu, Shashank Srivastava, and Snigdha Chaturvedi
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP Findings), 2024.
Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf], [code] -
Fuse to Forget: Bias Reduction and Selective Memorization through Model Fusion
Kerem Zaman, Leshem Chosen, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2024.
Learning and Language Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf], [code] -
DISCERN: Decoding Systematic Errors in Natural Language for Text Classifiers
Rakesh R Menon and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2024.
Learning and Language Fairness and Social Applications Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf], [code]
2023
-
Beyond Labels: Empowering Human Annotators with Natural Language Explanations through a Novel Active-Learning Architecture
Bingsheng Yao, Ishan Jindal, Lucian Popa, Yannis Katsis, Sayan Ghosh, Lihong He, Yuxuan Lu, Shashank Srivastava, Yunyao Li, James Hendler, and Dakuo Wang
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2023.
Active Learning
[pdf], [arxiv] -
Leveraging Multiple Teachers for Test-Time Adaptation of Language-Guided Classifiers
Kangda Wei, Sayan Ghosh, Rakesh R Menon, and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2023.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Pragmatic Reasoning Unlocks Quantifier Semantics for Foundation Models
Yiyuan Li, Rakesh R Menon, Sayan Ghosh, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2023.
Learning and Language Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Identifying and Manipulating the Perceived Personality Traits of Language Models
Graham Caron and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2023.
Fairness and Social Applications Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf], [arxiv] -
MaNtLE: Model-agnostic Natural Language Explainer
Rakesh R Menon, Kerem Zaman, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2023.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
LaSQuE: Improved Zero-Shot Classification from Explanations Through Quantifier Modeling and Curriculum Learning
Sayan Ghosh*, Rakesh R Menon*, and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2023.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models
Big-Bench Collaboration
Transactions of Machine Learning Research (TMLR), 2023.
Learning and Language Datasets and Benchmarks
[openreview], [pdf], [arxiv], [code], [dataset]
2022
-
What do Large Language Models Learn beyond Language?
Avinash Madasu and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2022.
Learning and Language
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Compositional Generalization for Kinship Prediction through Data Augmentation
Kangda Wei, Sayan Ghosh, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of the 4th Workshop of Narrative Understanding (WNU), 2022.
Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf], [code] -
Predicting Difficulty and Discrimination of Natural Language Questions
Matthew Byrd and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2022.
Language Understanding, Reasoning, and Generation Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf], [code], [dataset] -
ePiC: Employing Proverbs in Context as a Benchmark for Abstract Language Understanding
Sayan Ghosh and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2022.
Datasets and Benchmarks Language Understanding, Reasoning, and Generation Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf], [arxiv], [code], [dataset] -
CLUES: A Benchmark for Learning Classifiers using Natural Language Explanations
Rakesh R Menon*, Sayan Ghosh*, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2022.
Learning and Language Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf], [arxiv], [code], [dataset]
2021
-
Does Social Pressure Drive Persuasion in Online Fora?
Ayush Jain and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2021.
Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf] -
Mapping Language to Programs using Multiple Reward Components with Inverse Reinforcement Learning
Sayan Ghosh and Shashank Srivastava
Findings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2021.
Neuro-symbolic Learning
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Adversarial Scrubbing of Demographic Information for Text Classification
Somnath Basu Roy Chowdhury, Sayan Ghosh, Yiyuan Li, Junier B Oliva, Shashank Srivastava, and Snigdha Chaturvedi
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2021.
Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Improving and Simplifying Pattern Exploiting Training
Derek Tam*, Rakesh R Menon*, Mohit Bansal, Shashank Srivastava, and Colin Raffel
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2021.
Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
How Helpful is Inverse Reinforcement Learning for Table-to-Text Generation?
Sayan Ghosh*, Zheng Qi*, Snigdha Chaturvedi, and Shashank Srivastava
Proceedings of Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2021.
Language Understanding, Reasoning, and Generation
[pdf], [code]
2020
-
PRover: Proof Generation for Interpretable Reasoning over Rules
Swarnadeep Saha, Sayan Ghosh, Shashank Srivastava, and Mohit Bansal
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2020.
Language Understanding, Reasoning, and Generation
[pdf], [arxiv], [code] -
Learning Web-based procedures by Reasoning over Explanations and Demonstrations in Context
Shashank Srivastava, Oleksandr Polozov, Nebojsa Jojic, and Christopher Meek
Proceedings of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2020.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels Neuro-symbolic Learning Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf], [dataset] -
An Agent for Learning New Natural Language Commands
Amos Azaria, Shashank Srivastava, Jayant Krishnamurthy, Igor Labutov, and Tom Mitchell
Journal of Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (JAAMAS), 2020.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels
[link]
2019
-
Learning to Ask for Conversational Machine Learning
Shashank Srivastava, Igor Labutov, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2019.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf]
2018
-
LIA: A Natural Language Programmable Personal Assistant
Igor Labutov, Shashank Srivastava, and Tom Mitchell
Systems Demo, Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2018.
Learning and Language
[pdf] -
A Spatial Model for Extracting and Visualizing Latent Discourse Structure in Text
Shashank Srivastava and Nebojsa Jojic
Proceedings of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2018.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
Zero-shot Learning of Classifiers from Natural Language Quantification
Shashank Srivastava, Igor Labutov, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2018.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf] -
Where have I heard this story before? : Identifying Narrative Similarity in Movie Remakes
Snigdha Chaturvedi, Shashank Srivastava, and Dan Roth
Proceedings of the North Americal Chapter of Association of Computational Linguistics (NAACL), 2018.
Fairness and Social Applications Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf]
2017
-
Learning Classifiers from Declarative Language
Shashank Srivastava, Igor Labutov, and Tom Mitchell
NeurIPS Workshop on Learning from Limited Data, 2017.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels
[pdf] -
Joint Concept Learning and Semantic Parsing from Natural Language Explanations
Shashank Srivastava, Igor Labutov, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2017.
Learning and Language Learning from Limited Labels Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf] -
Parsing Natural Language Conversations with Contextual Cues
Shashank Srivastava, Amos Azaria, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), 2017.
Neuro-symbolic Learning Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf]
2016
-
CMUML Micro-Reader System for KBP 2016 Cold Start Slot Filling, Event Nugget Detection, and Event Argument Linking
Bishan Yang, Ndapandula Nakashole, Bryan Kisiel, Emmanouil A. Platanios, Abulhair Saparov, Shashank Srivastava, Derry Wijaya, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of the Text Analysis Conference (TAC), 2016.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
Inferring Interpersonal Relations in Narrative Summaries
Shashank Srivastava, Snigdha Chaturvedi, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2016.
Fairness and Social Applications Datasets and Benchmarks
[pdf] -
Modeling Evolving Relationships Between Characters in Literary Novel
Snigdha Chaturvedi, Shashank Srivastava, Hal Daume III, and Chris Dyer
Proceedings of the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2016.
Fairness and Social Applications
[pdf]
2015
-
CMU-ML System for KBP Cold Start Slot Filling
Bryan Kisiel, Bill McDowell, Matt Gardner, Ndapandula Nakashole, Emmanouil A. Platanios, Abulhair Saparov, Shashank Srivastava, Derry Wijaya, and Tom Mitchell
Proceedings of the Text Analysis Conference (TAC), 2015.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf]
2014
-
Vector space semantics with frequency-driven motifs
Shashank Srivastava and Eduard Hovy
Proceedings of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2014.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
Spatial Compactness meets Topical Consistency: Jointly modeling link and content for community detection
Mrinmaya Sachan, Avinava Dubey, Shashank Srivastava, Eric P Xing, and Eduard Hovy
Proceedings of Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM), 2014.
Miscellaneous
[pdf]
2013
-
A Walk-based Semantically Enriched Tree Kernel Over Distributed Word Representations
Shashank Srivastava, Dirk Hovy, and Eduard Hovy
Proceedings of Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), 2013.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
A Structured Distributional Semantic Model for Event Co-reference
Kartik Goyal*, Sujay Kumar Jauhar*, Huiying Li*, Mrinmaya Sachan*, Shashank Srivastava*, and Eduard Hovy
Proceedings of the Association of Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2013.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
A Structured Distributional Semantic Model : Integrating Structure with Semantics
Kartik Goyal*, Sujay Kumar Jauhar*, Huiying Li*, Mrinmaya Sachan*, Shashank Srivastava*, and Eduard Hovy
Workshop on Continuous Vector Space Models and their Compositionality, ACL, 2013.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf] -
Identifying Metaphorical Word Use with Tree Kernels
Dirk Hovy, Shashank Srivastava, Sujay Kumar Jauhar, Mrinmaya Sachan, Kartik Goyal, Huiying Li, Whitney Sanders, and Eduard Hovy
NAACL-HLT Meta4NLP Workshop, 2013.
Syntax and Semantics
[pdf]
2012
-
A Topical graph-kernel for Link Prediction in Labeled Graphs
Snigdha Chaturvedi, Hal Daume III, Taesun Moon, and Shashank Srivastava
ICML Workshop on Mining and Learning with Graphs (MLG), 2012.
Miscellaneous
[pdf]